 Applications of complementary operations on a sintered component allow to improve one or more characteristics not directly achievable from the basic process.
Applications of complementary operations on a sintered component allow to improve one or more characteristics not directly achievable from the basic process.
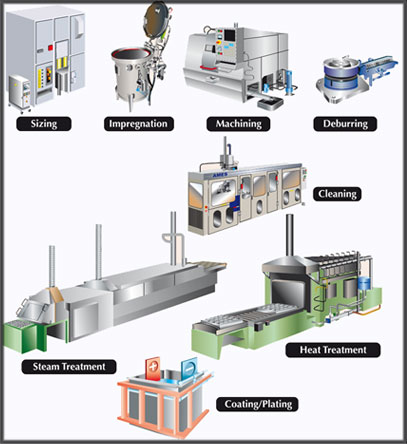
SIZING
It consists of compacting again the part inside a rigid mould which has the symmetrical opposite shape of the part. Sizing can have several purposes:
– Increasing the dimensional precision in diameter, reaching up to IT 5.
– Creating relief geometrical details not feasible in the compacted part, orimproving roughness.
– Densification. The applied densification degree is 7-10%, and it is also known as Coining.
OIL IMPREGNATION
Impregnation consists in filling pores with a chemical product:- Oil impregnation. Oil contained in the pores can act as lubricant of a bearing-shaft interface, hence self-lubrication is provided.
MACHINING
Sintered components can be sometimes machined when a shape or tolerance not achievable by compacting is required. Sintering support all conventional machining operations, ie., turning, milling, drilling, threading, grinding, lapping, reaming, polishing, and so forth.
DEBURRING
Deburring is applied to remove burrs inherent to compacting process. Burrs are removed either in bulk (tumbling, shot blasting, …), or on a unit basis (brushing, polishing, electrolytic deburring, …). Bulk deburring is sometimes used to provide an homogeneous surface aspect, or a very low roughness.
CLEANING
Cleaning operations are used to reduce or eliminate the amount of pollutants, solid or liquid, that a part may contain. There are many techniques, depending on material, type of pollutant, and required specifications.
STEAM TREATMENT
This is a thermal cycle of controlled oxidation of a steel, carried out in continuous furnaces with water steam. A magnetite layer coat is formed on the part surface and porosity. Its application on a component increases its compression strength, seals its porosity, and improves its environmental corrosion resistance.
HEAT TREATMENTS
A heat treatment is a thermal cycle that modifies the material properties. They are typically applied to increase hardness and strength of the component. The main surface or core heat treatments are: quenching, case hardening, and carbonitriding. Induction hardening is used to increase hardness in a local area of the part.
A particular case are the sinter-hardened components, which are made of a special type of steel that becomes hardened in the sintering furnace during the cooling.
COATING / PLATING
It is a material deposition on the component surface, which modifies the surface properties without changing the base metal chemical composition. Coatings are applied to fulfil functions under fatigue, wear, friction, or corrosion protection.
Sintered parts accept almost all conventional coatings, like zinc plating, chromium plating, nickel plating, phosphating, metallisation, PTFE, and other special coatings.

